Identifying Unmarked Banjos
Many banjo manufacturers, in addition to making banjos under their own names, made unmarked banjos for others to sell as well. In some cases, teachers would purchase these instruments and put their own names on them, but in many other cases they carry no identifying name at all. Itís difficult to positively identify the manufacturer of these banjos in many cases, but some identify themselves through common hardware and design characteristics. Another useful set of identifying characteristics can be found at http://www.mugwumps.com.
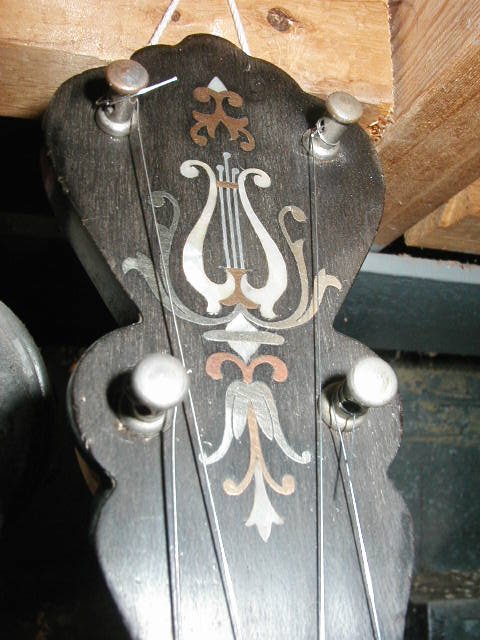
Buckbee (1861-1897) banjos can frequently be identified by their peghead shape. Banjos with pegheads like that shown in the first picture below are usually made by Buckbee.

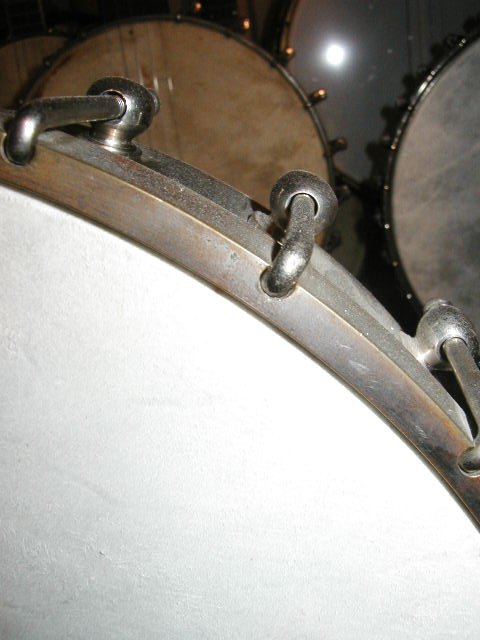
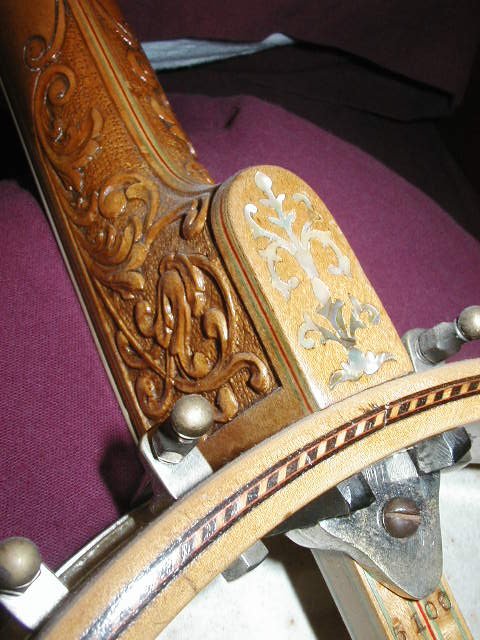
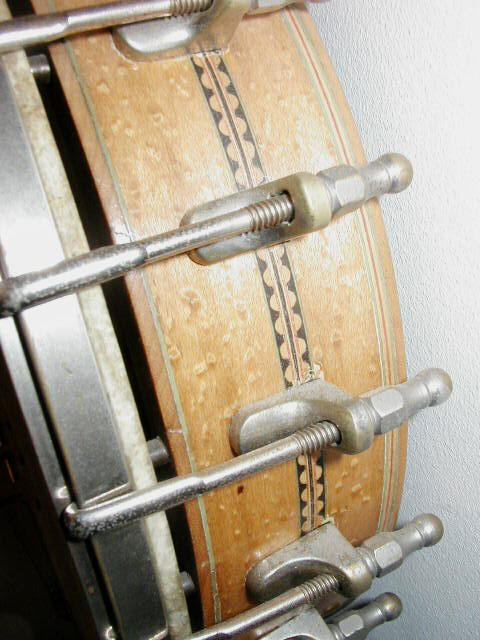
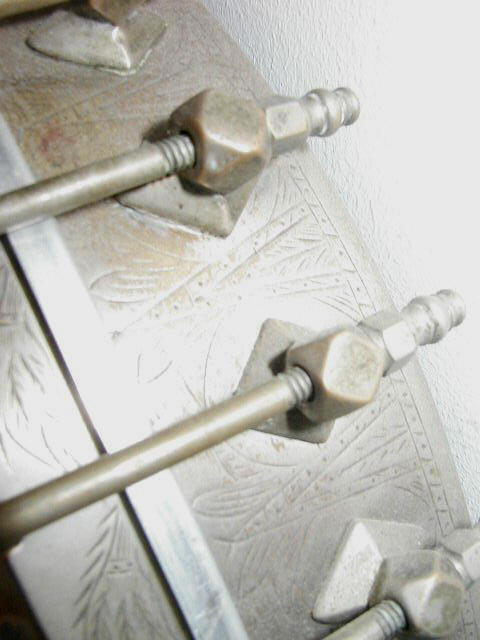
Rettberg & Lange (1898-1920) banjos were initially similar to Buckbee-made banjos, not surprising since they bought out the Buckbee factory in 1898. Most of their later banjos had elite tailpieces, Orpheum-like hardware, and long, thin heel footprints as shown below in the second row of pictures:
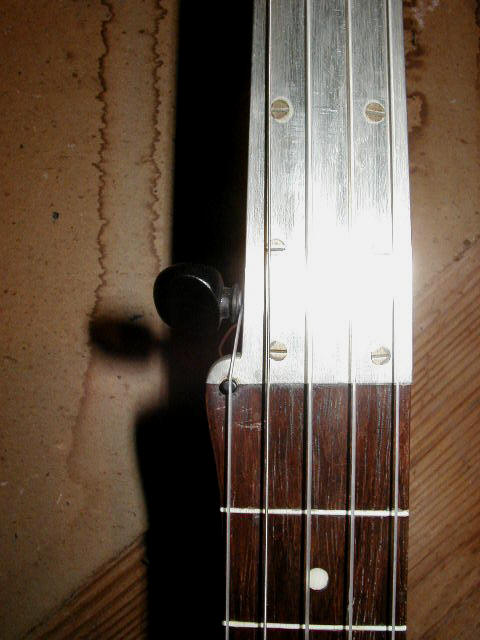
J. B. Schall (1878-1907) manufactured many unmarked banjos for teachers who sold them to students, some of which are tagged with the name of the teacher or distributor. Schall hardware is pretty unique and the fifth string peg perch is typically carved out from the side of the neck as shown in the third row of pictures below:
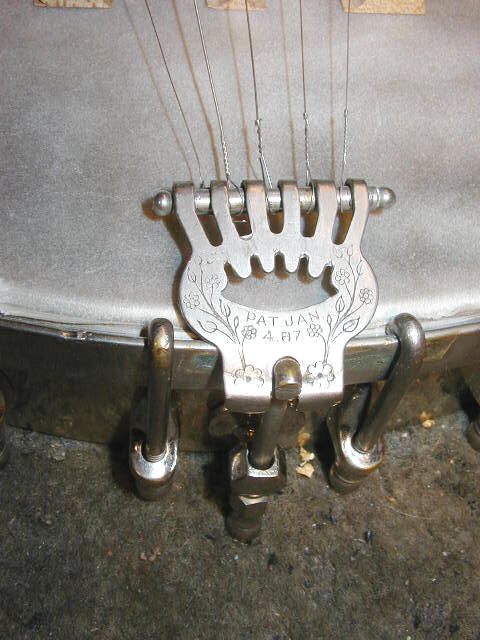
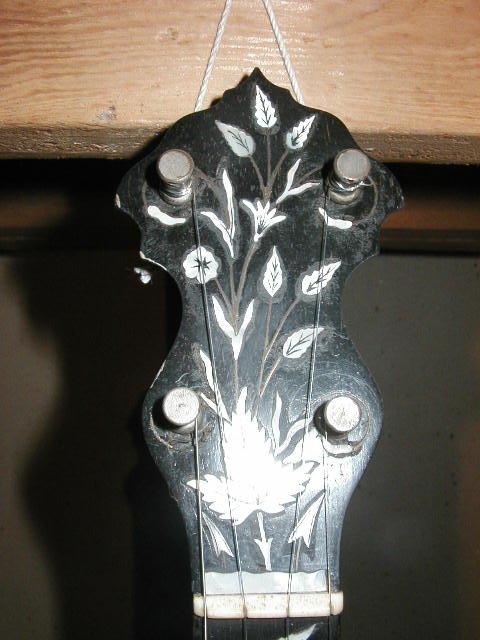
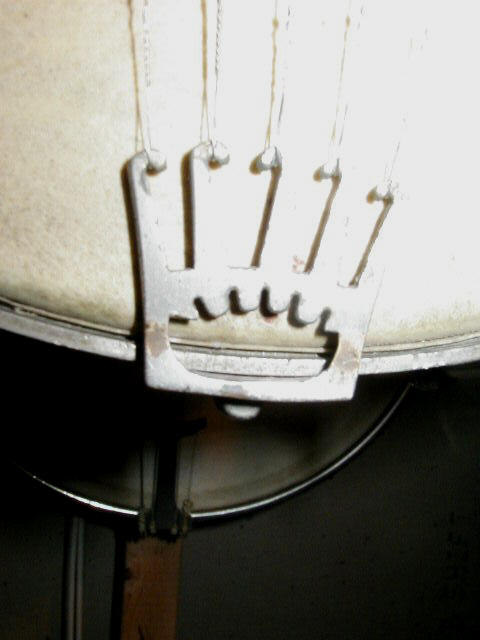
Lyon & Healy (1864-1940) made many grades of banjos in many styles, and many were left unmarked. Lyon & Healy routinely used talon or patent 1897 tailpieces (see fourth row of pictures below) on many of their unmarked banjos, and their better-grade offerings frequently had notched, rather than grooved stretcher bands even in the early 1890ís. The Lyon & Healy peghead shape used on most of their better banjos is also distinctive, with a small additional bump on either side of the top of the peghead (see last set of pictures below).




.